Palliative care is a specialized medical approach that focuses on enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing serious illnesses. It is not just about managing pain; it’s a holistic approach that addresses physical, emotional, and psychological needs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what palliative care is, when it’s appropriate, the dedicated team behind it, symptom management, emotional support, decision-making, receiving care at home, transitioning to hospice care, and valuable resources.
What is Palliative Care?
Palliative care is a patient-centered approach aimed at improving the well-being of individuals dealing with serious illnesses. Unlike hospice care, which is primarily for patients near the end of life, palliative care can be initiated at any stage of a serious illness. Its core principles include relieving pain and suffering, improving the overall quality of life, and providing support to both patients and their families.
When Is Palliative Care Appropriate?
Palliative care is appropriate when an individual is diagnosed with a serious illness, regardless of the stage. It can be provided alongside curative treatments to manage symptoms, relieve pain, and offer emotional support. Early integration of palliative care is associated with better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
The Palliative Care Team
A crucial aspect of palliative care is the interdisciplinary team. This team includes doctors, nurses, social workers, chaplains, and other specialists who work together to provide comprehensive care. Effective communication within the team ensures that the patient’s physical, emotional, and spiritual needs are met.
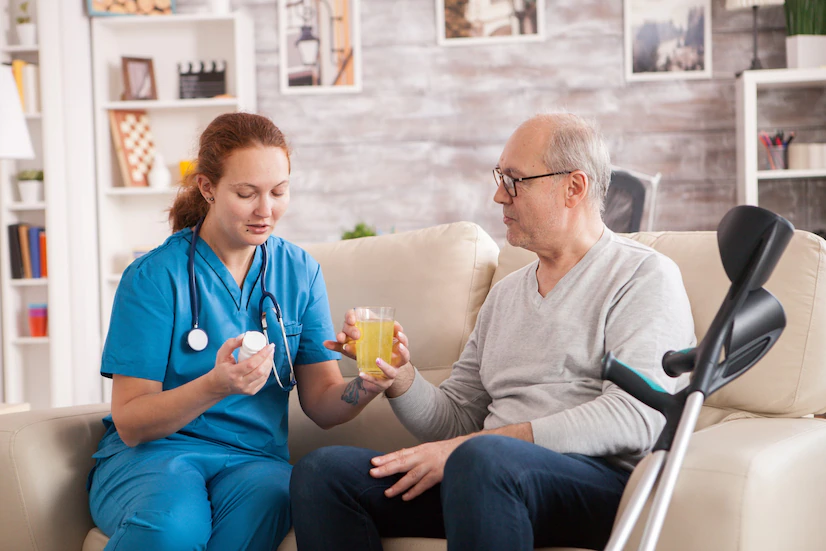
Assessing and Managing Symptoms
Patients receiving palliative care often experience a range of symptoms such as pain, nausea, fatigue, and anxiety. Palliative care specialists assess these symptoms and develop tailored treatment plans. Management approaches may include medications, physical therapy, relaxation techniques, and counseling to improve the patient’s comfort and well-being.
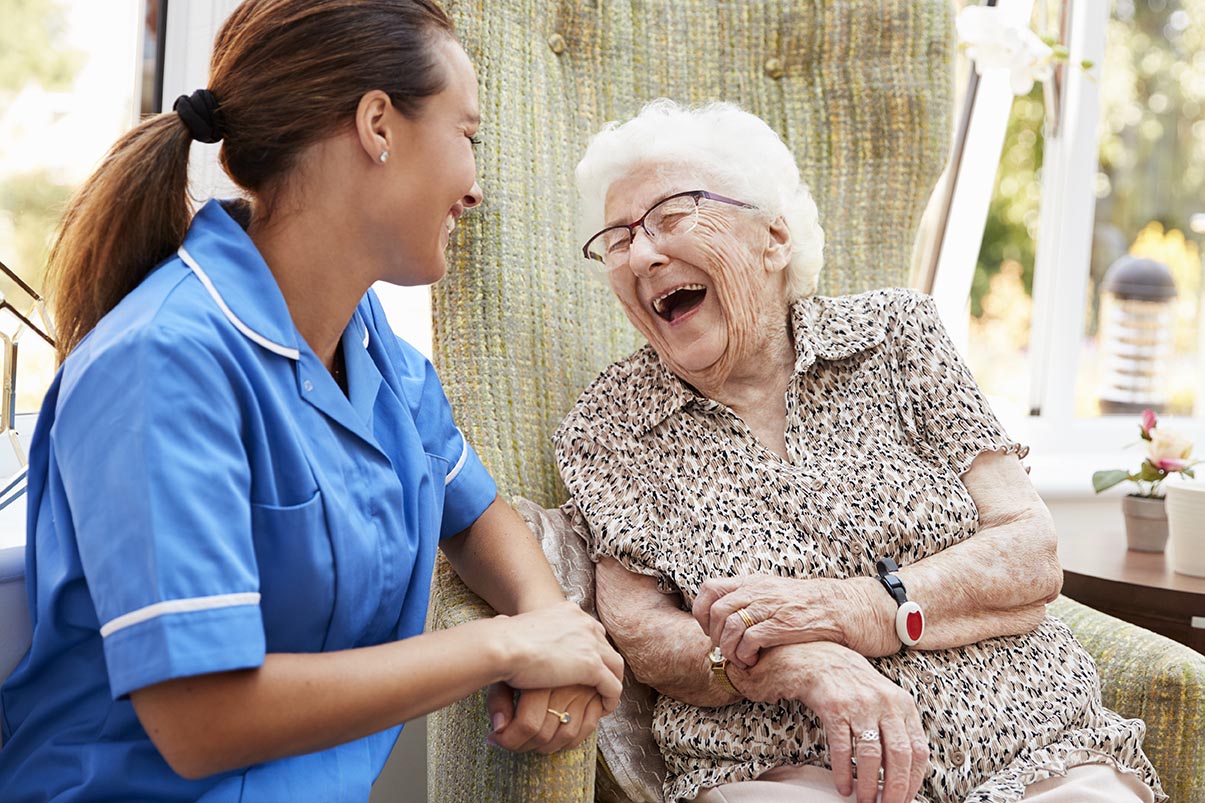
Emotional and Psychological Support
Serious illnesses can take a toll on a patient’s emotional and psychological well-being. Palliative care encompasses counseling, therapy, and support groups to help patients and their families cope with the emotional challenges that arise during the illness journey. This support is essential for maintaining a high quality of life.
Making Informed Decisions
Advance care planning and end-of-life discussions are essential components of palliative care. Patients and their families are encouraged to make informed decisions about their treatment preferences, goals of care, and resuscitation orders. These discussions ensure that care aligns with the patient’s values and wishes.
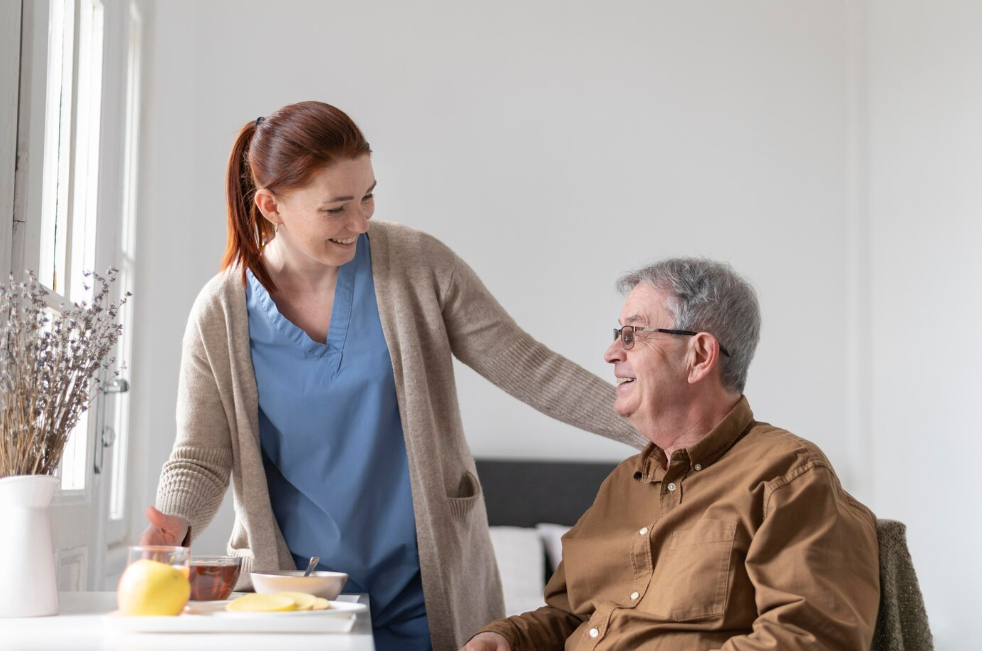
Palliative Care at Home
Many individuals prefer to receive palliative care in the comfort of their homes. This option allows patients to maintain their independence while receiving specialized care. Family caregivers play a crucial role in providing support, and home-based palliative care can enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Hospice Care Transition
At a certain point in a serious illness, patients may transition from palliative care to hospice care. While palliative care can continue alongside curative treatments, hospice care is focused on providing comfort and support in the final stages of life. Understanding the difference between the two and making a smooth transition is vital for the patient and their family.
Resources and Support
To navigate palliative care effectively, it’s essential to access the right resources and support. Numerous organizations and websites offer valuable information and guidance on palliative care. Additionally, local palliative care services and support groups can provide practical assistance and emotional support.
Takeaway
Palliative care is a compassionate and holistic approach to improving the quality of life for individuals facing serious illnesses. By understanding its principles, involving a dedicated care team, managing symptoms effectively, seeking emotional support, making informed decisions, considering home-based care, and transitioning to hospice care when necessary, patients and their families can navigate the complexities of palliative care more confidently.